이해가 되지 않는 부분은 아래의 코드처럼 카메라 생성 시 초기화로 카메라를 y축으로 180도 회전시켰는가… 이다.
cameraOrtho.rotation.y = Math.PI; cameraPerspective.rotation.y = Math.PI;
이 글의 예제 코드는 THREE.JS 공식 사이트의 EXAMPLES에서 제공되는 코드를 이해하고 제 나름대로의 코드로 재구성한 것입니다.

공간정보시스템 / 3차원 시각화 / 딥러닝 기반 기술 연구소 @지오서비스(GEOSERVICE)
이해가 되지 않는 부분은 아래의 코드처럼 카메라 생성 시 초기화로 카메라를 y축으로 180도 회전시켰는가… 이다.
cameraOrtho.rotation.y = Math.PI; cameraPerspective.rotation.y = Math.PI;
이 글의 예제 코드는 THREE.JS 공식 사이트의 EXAMPLES에서 제공되는 코드를 이해하고 제 나름대로의 코드로 재구성한 것입니다.
_initialize 함수를 보면 아래의 변수가 정의되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
this._splineHelperObjects = [];
this._positions = [];
this._splines = {};
_splineHelperObjects는 스플라인의 제어점에 대한 Mesh 객체를 담고 있습니다. _positions는 _splineHelperObjects에 저장된 Mesh들의 position 속성 객체들 항목으로 참조하고 있고 _splines은 key-value 컨테이너로 uniform, centripetal, chordal를 key로 하여 THREE.CatmullRomCurve3 객체를 value로 가집니다. 이때 이 value에 mesh를 속성으로하여 THREE.Line 객체를 갖습니다.
이 글의 예제 코드는 THREE.JS 공식 사이트의 EXAMPLES에서 제공되는 코드를 이해하고 제 나름대로의 코드로 재구성한 것입니다.
3차원에서는 다양한 3차원 객체가 Scene Graph 형태로 구성되어 있습니다. 렌더링하는 결과에 따라 그 형태가 매우 복잡하게 구성될 수 있는데.. Scene Graph의 구성 요소를 확인하기 위한 간단한 함수입니다.
dumpVec3(v3, precision = 3) {
return `${v3.x.toFixed(precision)}, ${v3.y.toFixed(precision)}, ${v3.z.toFixed(precision)}`;
}
dumpObject(obj, lines = [], isLast = true, prefix = '') {
const localPrefix = isLast ? '└─' : '├─';
lines.push(`${prefix}${prefix ? localPrefix : ''}${obj.name || '*no-name*'} [${obj.type}]`);
const dataPrefix = obj.children.length
? (isLast ? ' │ ' : '│ │ ')
: (isLast ? ' ' : '│ ');
lines.push(`${prefix}${dataPrefix} pos: ${this.dumpVec3(obj.position)}`);
lines.push(`${prefix}${dataPrefix} rot: ${this.dumpVec3(obj.rotation)}`);
lines.push(`${prefix}${dataPrefix} scl: ${this.dumpVec3(obj.scale)}`);
const newPrefix = prefix + (isLast ? ' ' : '│ ');
const lastNdx = obj.children.length - 1;
obj.children.forEach((child, ndx) => {
const isLast = ndx === lastNdx;
this.dumpObject(child, lines, isLast, newPrefix);
});
return lines;
}
사용은 다음과 같습니다.
console.log(this.dumpObject(root).join('\n'));
결과 예는 다음과 같습니다.
*no-name* [Scene]
│ pos: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ scl: 1.000, 1.000, 1.000
├─*no-name* [DirectionalLight]
│ pos: -250.000, 800.000, -850.000
│ rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ scl: 1.000, 1.000, 1.000
├─*no-name* [Object3D]
│ pos: -550.000, 40.000, -450.000
│ rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ scl: 1.000, 1.000, 1.000
...
├─*no-name* [Object3D]
│ │ pos: 571.897, -76.040, -1163.608
│ │ rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ │ scl: 1.000, 1.000, 1.000
│ └─CAR_03_3 [Object3D]
│ │ pos: 0.000, 33.000, 0.000
│ │ rot: 0.000, 3.142, 0.000
│ │ scl: 1.500, 1.500, 1.500
│ └─CAR_03_3_World_ap_0 [Mesh]
│ pos: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
│ scl: 1.000, 1.000, 1.000
└─*no-name* [Line]
pos: 0.000, -621.000, 0.000
rot: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
scl: 100.000, 100.000, 100.000
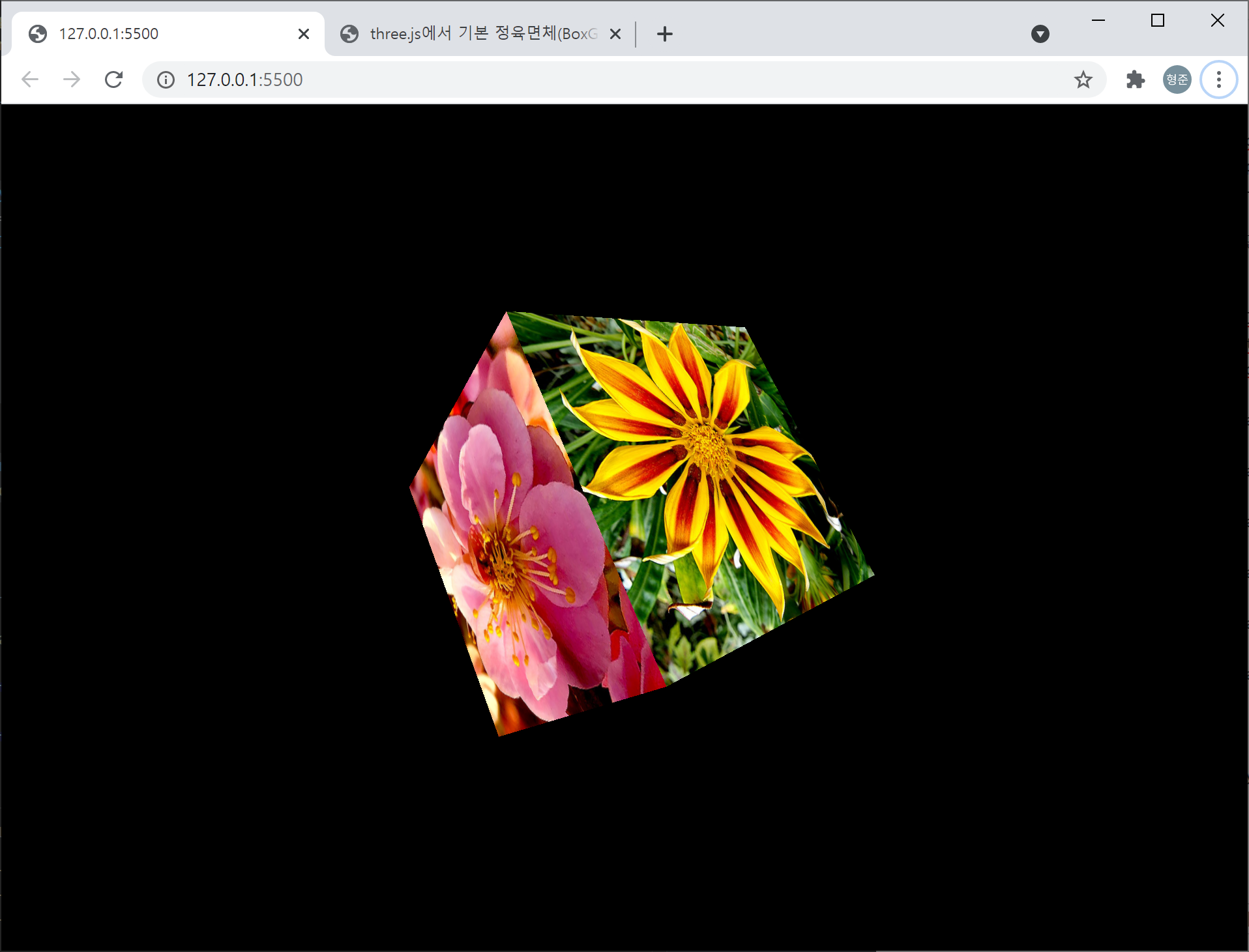
three.js에서 제공하는 기본 정육면체에 대해 텍스쳐 맵핑을 하는 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: loader.load("flower-5.jpg", undefined, undefined, function(err) {
alert('Error');
}),
});
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
this.scene.add(cube);
실행하면 다음과 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
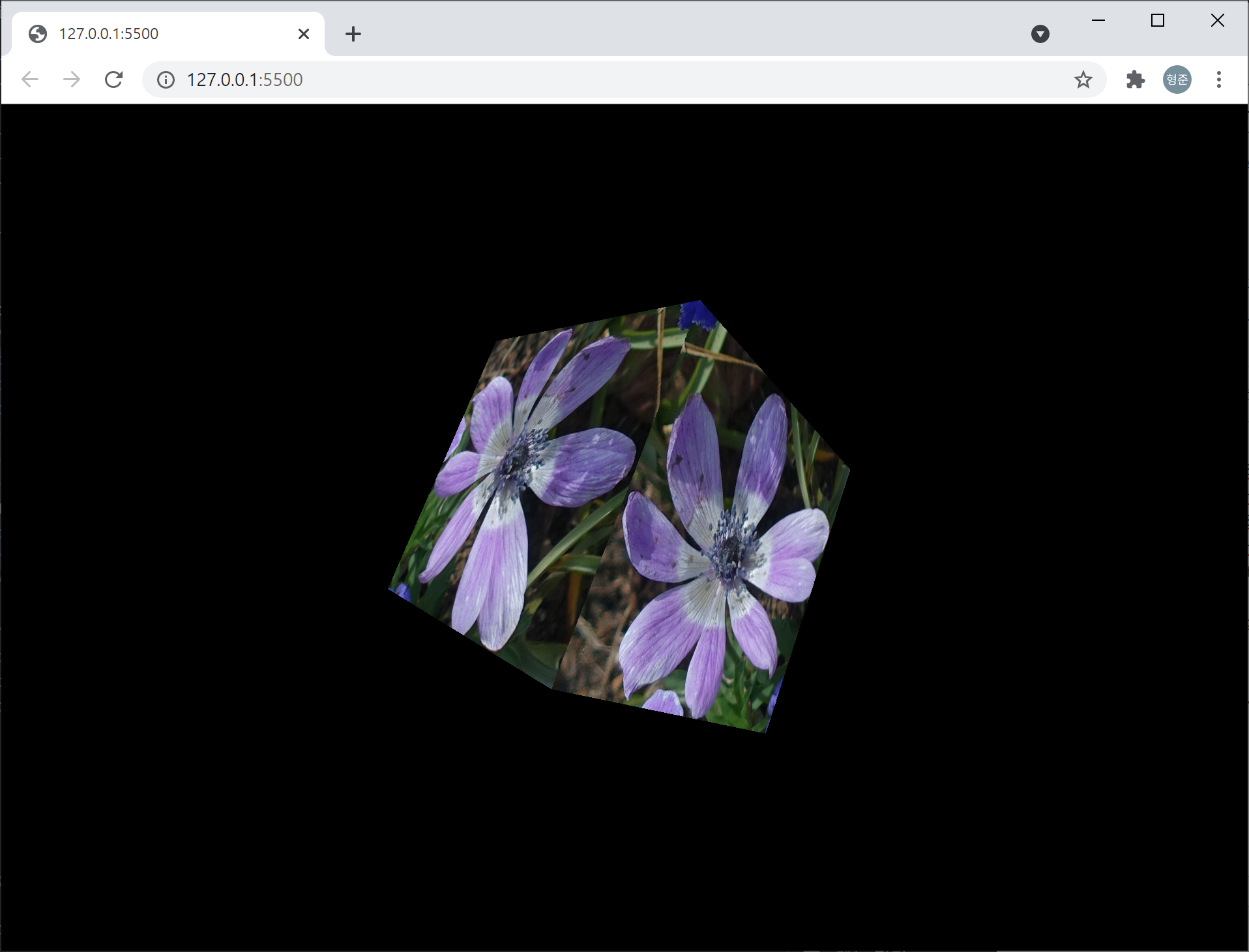
그런데 이 THREE.BoxGeometry는 각 면에 대해 다른 텍스쳐 맵핑을 지정할 수 있습니다. 아래처럼요.
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const materials = [
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-1.jpg") }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-2.jpg") }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-3.jpg") }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-4.jpg") }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-5.jpg") }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: loader.load("flower-6.jpg") }),
];
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, materials);
this.scene.add(cube);
결과는 다음과 같습니다.
이 글은 three.js의 전체 코드가 아닌 정육면체에 텍스쳐 맵핑에 대한 코드만을 언급하고 있습니다. 전체 코드에 대한 뼈대는 아래 글을 참고 하시기 바랍니다. 위의 코드들은 모두 _setupModel 함수의 코드입니다.